Industrial Automation Tools
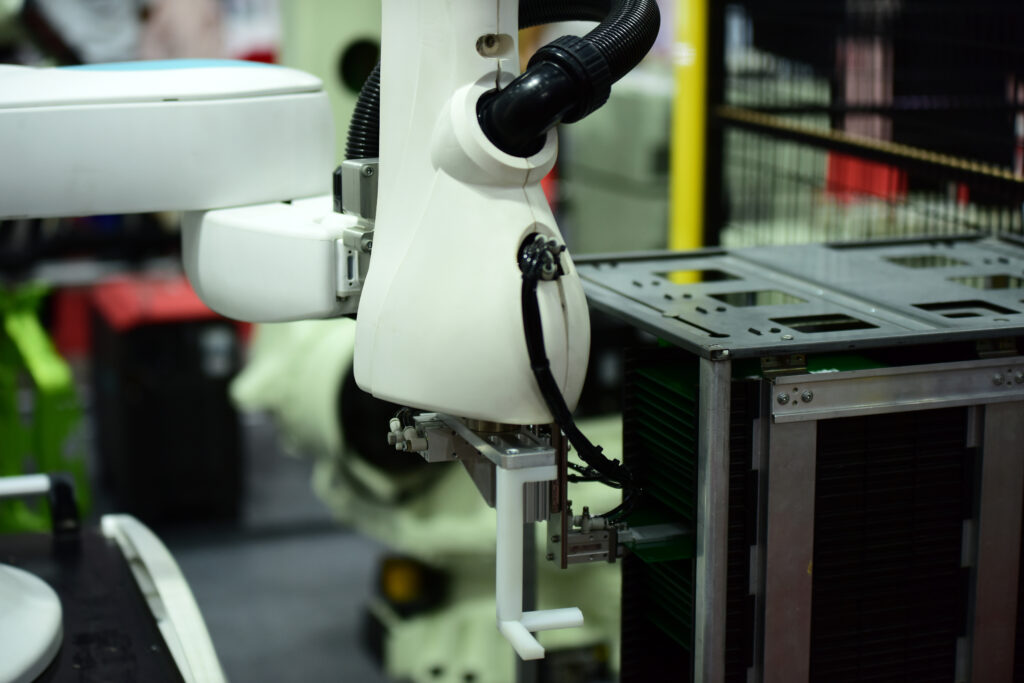

Industrial automation tools are the engines of modern manufacturing and process industries. They enable companies to reduce downtime, enhance quality, and increase throughput, while ensuring safety and sustainability. As industries move toward digital transformation, tools such as programmable controllers, SCADA systems, robotics, sensors, and IIoT platforms form the foundation of the smart factory. These tools not only automate tasks but also provide real-time data, predictive insights, and seamless integration between operational technology and business systems. With the right selection and deployment, companies achieve a competitive edge in the Industry 4.0 era. Core Categories Of Industrial Automation Tools Industrial automation relies on a diverse set of tools, each serving a unique role in monitoring, controlling, and optimizing processes. Together, they form a layered ecosystem that drives efficiency and innovation. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) PLCs are the cornerstone of industrial automation. They control machines and processes by executing programmed instructions in real time. Modern PLCs support advanced networking, motion control, and modular expansion. Their reliability makes them indispensable for assembly lines, material handling, and process control. Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) HMIs provide operators with visual dashboards to monitor and control systems. Through intuitive screens, workers can view machine states, adjust parameters, and respond to alarms quickly. Touch-based HMIs with rich graphics improve usability and reduce operator error. Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition (SCADA) SCADA systems oversee multiple processes and sites by collecting data from PLCs and sensors. They offer trending, alarm management, and centralized visualization, making them critical for utilities, oil and gas, and large-scale manufacturing. Modern SCADA integrates with cloud platforms for remote monitoring and analytics. Distributed Control Systems (DCS) DCS platforms are used in continuous process industries such as chemicals and power generation. They distribute control functions across multiple nodes, ensuring reliability and scalability. DCS provides redundancy, advanced process control, and high availability for mission-critical operations. Industrial Robotics Robots handle repetitive, dangerous, or high-precision tasks. From robotic arms in automotive welding to pick-and-place units in logistics, robotics increases speed and reduces defects. Collaborative robots (cobots) now work safely alongside humans, enhancing flexibility in production environments. Sensors And Actuators Sensors gather real-time data on temperature, pressure, flow, vibration, and position, while actuators perform physical actions such as movement or force application. These devices form the “nervous system” of automation, connecting the physical world to digital control systems. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) Platforms IIoT platforms connect machines, devices, and systems across factories. They collect and analyze massive data streams, supporting predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and real-time decision-making. Combined with AI, IIoT platforms drive the digital twin concept, enabling simulations and continuous improvement. Motion Control Systems Motion controllers, drives, and servo motors ensure precise movement in machine tools, conveyors, and robotic arms. High-speed motion control enhances productivity in packaging, electronics manufacturing, and aerospace applications. Advanced Tools Driving Industry 4.0 In addition to traditional tools, emerging technologies are transforming the landscape of automation. Artificial Intelligence And Machine Learning AI-enabled automation tools optimize processes by learning from historical data and predicting future trends. Machine learning algorithms detect anomalies, suggest parameter adjustments, and support autonomous decision-making in dynamic environments. Digital Twins Digital twin technology creates virtual replicas of machines and systems. These models simulate performance, predict failures, and test new configurations without disrupting production. Combined with real-time data, they enable continuous optimization. Cloud And Edge Computing Cloud platforms enable centralized data analysis and integration with enterprise systems, while edge computing provides real-time processing near machines. Together, they reduce latency, enhance security, and improve resilience against connectivity issues. Industrial Cybersecurity Tools Cybersecurity is essential in connected factories. Tools such as intrusion detection, secure gateways, and network segmentation protect critical infrastructure from cyberattacks. Adopting IEC 62443 standards ensures industrial systems remain resilient. Benefits Of Industrial Automation Tools The adoption of automation tools yields measurable outcomes across industries, providing both operational and strategic advantages. Increased Efficiency And Productivity Automation tools reduce cycle times, eliminate manual errors, and allow 24/7 production. Companies achieve higher throughput and more consistent quality with fewer resources. Reduced Downtime Predictive analytics and condition monitoring detect issues before they cause failures. Automated fault diagnostics accelerate recovery, minimizing production losses. Improved Safety By automating hazardous tasks, industrial tools protect workers from accidents. Safety systems integrated with PLCs and robotics ensure compliance with standards and safeguard human operators. Sustainability And Energy Optimization Automation reduces waste, lowers energy consumption, and supports environmental goals. Tools that monitor resource usage help companies meet ESG commitments and regulatory requirements. Challenges In Using Automation Tools While powerful, automation tools present certain challenges that must be addressed strategically. Integration With Legacy Systems Many factories operate with decades-old equipment. Integrating modern tools without disrupting production requires careful planning and custom solutions. Skill Gaps Workforces often lack expertise in advanced automation tools. Training programs and user-friendly interfaces are necessary to maximize value from new technologies. Cybersecurity Risks Increased connectivity exposes systems to cyber threats. Security-by-design is essential for preventing downtime and data breaches. Industries Leveraging Automation Tools Industrial automation tools are applied across diverse industries, each with distinct requirements. Automotive And Aerospace Robotics, PLCs, and digital twins optimize assembly lines, ensure traceability, and enable precision manufacturing in these high-demand sectors. Pharmaceuticals And Life Sciences Automation tools ensure compliance with GMP standards, improve quality control, and support electronic batch records. Food And Beverage SCADA and sensors guarantee consistency, traceability, and hygiene. Robotics handle packaging and sorting efficiently. Energy And Utilities DCS and SCADA systems optimize power generation, water treatment, and oil refining. Predictive maintenance ensures reliability of critical infrastructure. Why Bilgeweb Is A Trusted Automation Partner Bilgeweb stands out by offering consulting, integration, and lifecycle support for industrial automation tools. The company’s vendor-agnostic approach ensures the best-fit solutions without lock-in. With expertise in AI, IoT, and automation engineering, Bilgeweb delivers platforms that scale with business needs and future trends. Comprehensive Expertise Bilgeweb supports every layer of automation, from PLC programming to IIoT deployment. Its cross-domain experience ensures solutions are robust, secure, and future-ready. Data-Driven And AI-Ready Bilgeweb integrates data models and analytics into automation tools, empowering
Defense Embedded Systems
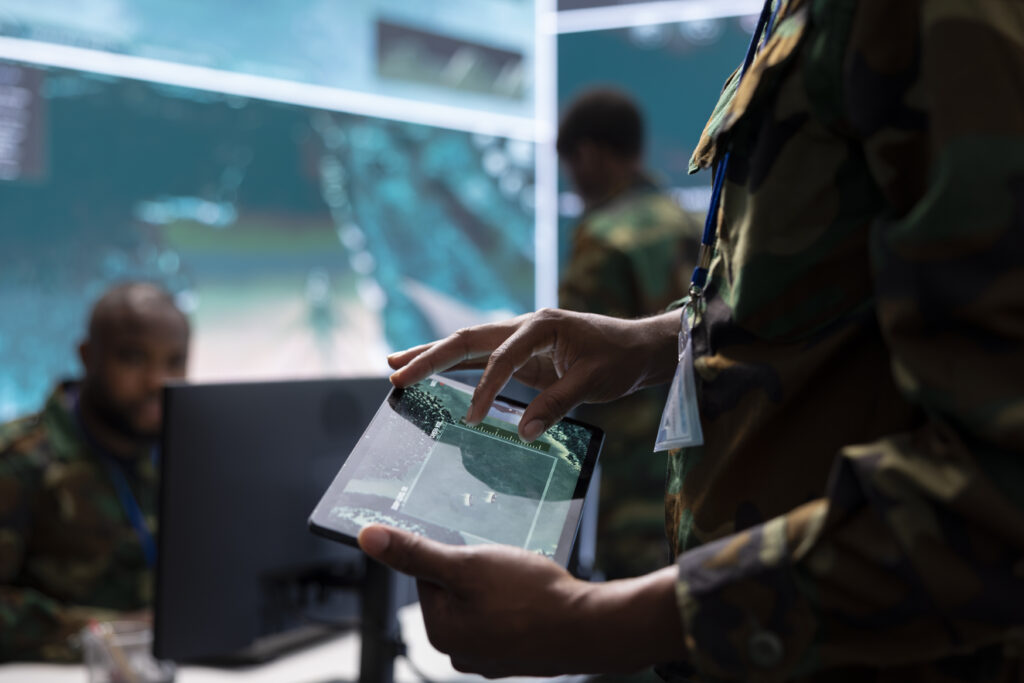

Defense embedded systems form the invisible backbone of modern military technology. These specialized computing units power mission-critical functions such as avionics, radar, electronic warfare, secure communications, and weapons control. Unlike commercial systems, defense embedded platforms must operate reliably under extreme conditions—high altitude, high radiation, electromagnetic interference, and cyber threats. They are designed for real-time performance, ruggedness, and long lifecycles, making them indispensable to armed forces worldwide. With innovation in AI, IoT, and cybersecurity, embedded systems are becoming smarter, more connected, and more adaptive to the evolving battlefield. What Are Defense Embedded Systems Embedded systems in defense are purpose-built hardware and software units integrated into larger military platforms. Their role is to process sensor data, run control algorithms, and provide secure communication channels in real time. Unlike general-purpose computers, they are optimized for reliability, low latency, and survivability in mission environments. Key Characteristics Real-time performance: They execute instructions within strict deadlines to ensure accurate responses in combat. Rugged design: Hardware withstands shock, vibration, temperature extremes, and electromagnetic interference. Long lifecycle support: Defense programs may last decades, so embedded systems must be maintainable and upgradeable over time. Cybersecurity hardened: Secure boot, encryption, and anomaly detection prevent adversaries from compromising systems. Applications Of Embedded Systems In Defense Embedded systems enable a wide range of defense operations across air, land, sea, space, and cyber domains. Avionics And Aerospace In aircraft, embedded systems manage flight control, navigation, engine monitoring, and communication. Fly-by-wire systems rely on embedded processors to ensure stability and safety, while mission computers handle target acquisition and weapons release. Radar And Electronic Warfare Radar systems depend on embedded processors to filter signals, identify targets, and detect threats. In electronic warfare, embedded platforms manage jamming, spoofing, and countermeasure deployment in real time. Weapons Control And Guidance Embedded computers guide missiles, control fire systems on naval vessels, and synchronize artillery operations. Precision and reliability are paramount to ensure mission success with minimal collateral impact. Secure Communications Military communication devices use embedded cryptographic modules to secure voice, video, and data transmissions. Embedded platforms enforce authentication and encryption, preventing interception or tampering by adversaries. Unmanned Systems Drones, autonomous ground vehicles, and underwater robots rely heavily on embedded controllers for navigation, sensor integration, and AI-based decision-making. These systems expand military reach while reducing risks to human personnel. Technological Enablers Defense embedded systems leverage cutting-edge technology to maintain superiority in contested environments. Artificial Intelligence And Machine Learning AI-powered embedded processors allow real-time target recognition, predictive maintenance, and autonomous decision-making. These capabilities enhance speed and precision in combat operations. Edge Computing Instead of relying on distant servers, embedded systems process data locally at the “edge.” This reduces latency and ensures continued functionality even when communications are degraded or jammed. Advanced Processors And FPGAs Custom processors and reprogrammable FPGAs provide the speed and flexibility required for evolving defense missions. FPGAs enable cryptographic agility and real-time signal processing for radar and communications. Cybersecurity Integration With cyber warfare escalating, embedded systems now incorporate built-in security—secure boot mechanisms, intrusion detection, and hardware-based encryption. Defense systems cannot afford to be compromised in mission-critical scenarios. Challenges Facing Defense Embedded Systems Despite their sophistication, embedded systems face unique hurdles that require careful engineering and governance. Harsh Environments Military platforms operate in deserts, oceans, outer space, and battlefields. Embedded systems must continue functioning despite extreme temperature shifts, pressure, or exposure to radiation. Interoperability With Legacy Systems Defense forces often integrate new embedded solutions with legacy equipment. Ensuring compatibility while maintaining performance and security is a major challenge. Supply Chain Security Global chip shortages and supply chain vulnerabilities raise concerns about counterfeit or compromised components. Defense programs increasingly focus on secure, verified supply chains. Long Development And Lifecycle Defense systems often remain in service for 20+ years. Embedded solutions must allow modular upgrades to prevent obsolescence while meeting evolving standards. Industries And Programs That Depend On Embedded Systems Defense embedded systems span all branches of military operations. Air Defense And Missile Systems Missile guidance and interceptor platforms rely on embedded control systems for speed, accuracy, and synchronization with radar networks. Naval Platforms Warships and submarines use embedded systems for sonar, weapons control, propulsion monitoring, and secure communication. Reliability is critical for long missions at sea. Ground Vehicles Armored vehicles integrate embedded systems for navigation, targeting, and health monitoring. Autonomous capabilities are increasingly added through AI-enabled processors. Space And Satellite Systems Satellites used for navigation, reconnaissance, and communication depend on radiation-hardened embedded electronics that can function in orbit for decades. Why Bilgeweb Is A Strategic Partner Bilgeweb stands out as a defense technology partner by combining software expertise, automation knowledge, and security-first design. With a track record in industrial automation and AI-driven platforms, Bilgeweb applies its engineering excellence to the defense sector, delivering embedded systems that are secure, efficient, and mission-ready. Security-First Design Bilgeweb designs embedded solutions with hardened cybersecurity at the core—ensuring that every system resists intrusions, tampering, and data leakage. Secure coding practices, real-time monitoring, and encryption are built in from day one. Cross-Domain Expertise Drawing from expertise in automation, AI, and software integration, Bilgeweb creates embedded platforms adaptable to aerospace, naval, ground, and cyber defense missions. This versatility enables clients to adopt technologies that meet both present and future needs. Vendor-Agnostic And Modular Bilgeweb avoids lock-in by developing modular architectures and open standards. Defense clients retain flexibility to expand or adapt systems without overhauling entire infrastructures. Commitment To Long-Term Support With defense projects lasting decades, Bilgeweb provides lifecycle support, ensuring that embedded systems remain reliable, secure, and up-to-date with evolving mission requirements. Defense embedded systems are the silent enablers of mission success—powering avionics, radar, weapons, communications, and autonomous platforms. By partnering with Bilgeweb, defense organizations gain access to secure, scalable, and future-ready embedded solutions designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern warfare. In an era where speed, reliability, and cybersecurity define military advantage, embedded systems engineered by Bilgeweb deliver performance where it matters most.
Industrial Automation Consulting
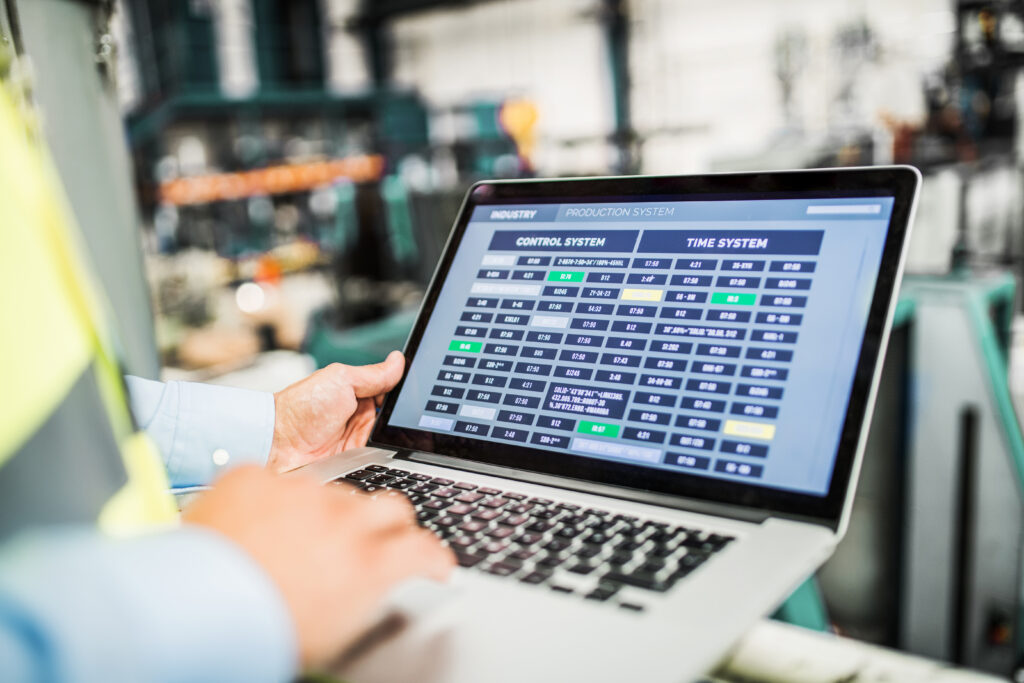

As global industries push for higher efficiency, better product quality, and sustainable growth, the role of industrial automation consulting has never been more critical. Companies are no longer asking if they should automate but how to do so intelligently, cost-effectively, and sustainably. Industrial automation consulting services provide the roadmap for businesses navigating this transformation—guiding them through technology choices, integration challenges, and long-term performance optimization. With expert consultants, organizations unlock new value streams, achieve competitive advantage, and reduce the risks that come with complex automation projects. The Role Of Industrial Automation Consulting Consulting in automation goes beyond simply recommending technologies. It involves understanding an organization’s production processes, identifying bottlenecks, analyzing costs, and aligning technology adoption with strategic business goals. The objective is to create a holistic automation strategy that delivers measurable improvements across safety, productivity, and profitability. Process Assessment And Gap Analysis The first step in any consulting engagement is a deep dive into current operations. Consultants analyze machine uptime, OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness), scrap rates, energy consumption, and labor allocation. A gap analysis compares the present state with industry benchmarks and future goals. This sets the foundation for a realistic and high-impact automation roadmap. Technology Selection And Vendor Evaluation The automation market is crowded with options—PLCs, SCADA, MES, robotics, AI, and IIoT platforms. An independent consultant ensures technology choices are vendor-agnostic and suited to the client’s specific requirements. The evaluation covers lifecycle costs, scalability, cybersecurity, and interoperability with legacy systems. Integration Strategy Integration is often the hardest part of automation. Legacy equipment, proprietary protocols, and siloed data structures make projects risky. Consulting services define integration strategies that align OT (Operational Technology) with IT, enabling data to flow seamlessly between shop-floor machines and enterprise platforms like ERP and CMMS. This IT/OT convergence is a cornerstone of Industry 4.0. Key Services In Industrial Automation Consulting Automation consulting spans a wide range of services that help organizations move from strategy to execution while managing risk and costs effectively. Digital Transformation And Industry 4.0 Consultants help businesses adopt digital tools such as IIoT, edge computing, AI-driven analytics, and cloud integration. These technologies allow predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and real-time visibility across production lines. A clear transformation roadmap minimizes disruption while maximizing long-term ROI. Safety And Compliance Consulting Safety is non-negotiable in industrial environments. Consulting includes risk assessments, safety circuit design, and compliance with international standards like ISO 13849, IEC 62061, and OSHA regulations. Safety consulting ensures that automation not only boosts productivity but also protects workers and assets. Cybersecurity Advisory Industrial automation systems are frequent targets of cyber threats. Consultants assess vulnerabilities, recommend segmentation, apply IEC 62443 standards, and design zero-trust architectures. Strong cybersecurity consulting ensures resilience against ransomware, state-sponsored attacks, and insider threats. Lifecycle And Change Management Automation projects are long-term investments. Consulting services extend to lifecycle management, ensuring systems remain up-to-date and optimized. Change management addresses cultural resistance by training operators and maintenance staff, ensuring smooth adoption of new technologies. Benefits Of Industrial Automation Consulting Businesses engaging in consulting services gain a strategic edge by avoiding common pitfalls and accelerating automation maturity. Cost Savings And Efficiency By optimizing processes and introducing smart automation, companies achieve higher throughput, lower scrap, and reduced downtime. These improvements translate directly into financial savings and faster payback periods. Improved Decision-Making With real-time data and predictive analytics, managers gain visibility into performance metrics. This enables proactive decision-making, better resource allocation, and more accurate demand forecasting. Sustainability And Energy Efficiency Consultants design solutions that optimize energy use, reduce emissions, and support compliance with environmental regulations. This not only improves ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) performance but also lowers operational costs. Scalability And Flexibility Consulting ensures that automation investments are scalable. Modular designs and open architectures allow businesses to expand capacity or introduce new product lines without major overhauls. Challenges In Industrial Automation Consulting While consulting provides clear benefits, organizations face challenges that must be carefully addressed to ensure success. Resistance To Change Employees may view automation as a threat to jobs. Consultants develop communication and training strategies that emphasize how automation enhances rather than replaces human roles. Budget Constraints Automation can involve significant upfront costs. Consulting ensures that investments are phased, prioritized, and justified by clear ROI projections, making them more palatable for decision-makers. Technology Overload Adopting too many new technologies too quickly can overwhelm organizations. Consultants prevent “shiny object syndrome” by aligning adoption with measurable goals and readiness levels. Industries Benefiting From Automation Consulting Industrial automation consulting applies to multiple sectors, each with unique requirements and challenges. Automotive And Aerospace Consulting focuses on precision, traceability, and advanced robotics integration. Predictive analytics ensure uptime in high-volume, high-complexity environments. Pharmaceuticals And Life Sciences Automation consulting ensures compliance with FDA, EMA, and GMP regulations. Electronic batch records, validated software, and data integrity are top priorities. Food And Beverage Consultants help design hygienic, traceable automation systems that minimize waste and ensure consistency in batch production. Energy management and CIP optimization are common priorities. Oil, Gas, And Energy Automation consulting improves safety in hazardous environments while optimizing production and distribution. Remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and SCADA optimization are key focus areas. Why Bilgeweb Is The Ideal Consulting Partner Bilgeweb is a trusted name in industrial automation consulting, with expertise spanning multiple industries and technologies. The company’s consulting philosophy emphasizes measurable outcomes, long-term support, and open, future-ready architectures. Vendor-Agnostic Approach Bilgeweb evaluates technologies objectively, ensuring clients receive the best-fit solutions without vendor lock-in. This flexibility protects long-term investment value. Cross-Domain Expertise With experience in automation, AI, Web3, and software integration, Bilgeweb delivers solutions that are technically sound and strategically aligned with business goals. This cross-domain knowledge enables truly innovative consulting outcomes. Proven ROI Delivery Bilgeweb emphasizes ROI-focused consulting. Every recommendation ties back to performance metrics such as OEE, energy intensity, and maintenance costs, ensuring tangible business results. Commitment To Client Success From initial assessment to lifecycle support, Bilgeweb acts as a long-term partner. Clients benefit from continuous improvement, training, and proactive system monitoring to sustain competitive advantage. Industrial automation consulting is the catalyst for
Defense Software Platforms
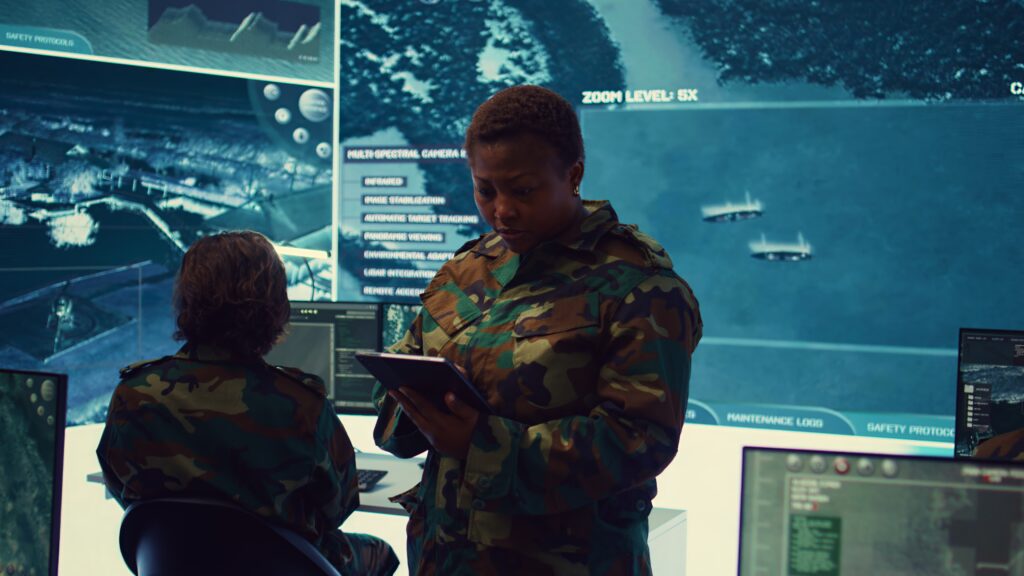

Defense organizations face growing complexity in mission operations, cybersecurity threats, and integration of emerging technologies. To maintain strategic advantage, modern armed forces rely on robust defense software platforms that combine interoperability, data fusion, and mission readiness. These platforms are no longer isolated systems—they form a digital ecosystem that connects sensors, shooters, decision-makers, and allies in real time. With secure architectures and modular design, defense software platforms ensure that military units can act with speed, precision, and coordination under any scenario. Core Functions Of Defense Software Platforms Defense software platforms serve as the backbone of military operations. Their scope ranges from battlefield management and logistics planning to intelligence processing and cybersecurity. By unifying data and automating workflows, they help commanders shorten decision cycles while increasing situational awareness. Command And Control Systems Modern C2 platforms integrate multi-domain operations—land, sea, air, cyber, and space—into a single operational picture. They allow commanders to see friendly and adversary positions, allocate resources, and coordinate missions with precision. Features include secure communications, tactical data links, and AI-driven decision aids that support rapid course-of-action analysis. Intelligence, Surveillance, And Reconnaissance (ISR) ISR platforms collect and process data from satellites, UAVs, radar, and human intelligence. Advanced analytics transform raw data into actionable insights, allowing forces to anticipate threats and plan effectively. Real-time sensor fusion provides a comprehensive view of the battlespace, minimizing blind spots. Cybersecurity And Information Assurance Defense platforms must resist sophisticated cyberattacks. Secure operating environments, intrusion detection systems, and encrypted communications are critical. Zero-trust architectures and continuous monitoring ensure that adversaries cannot exploit vulnerabilities within command networks or weapon systems. Simulation And Training Systems Simulation platforms provide realistic, cost-effective training for soldiers, pilots, and commanders. They model combat environments, weapon behavior, and tactical scenarios. Integrated with VR/AR, these platforms prepare personnel for complex missions without the risk and expense of live exercises. Key Technological Enablers The effectiveness of defense software platforms depends on integration with advanced technologies. Cutting-edge tools enhance speed, scalability, and decision quality. Artificial Intelligence And Machine Learning AI-driven algorithms support target recognition, threat prediction, and logistics optimization. Machine learning continuously adapts to adversary tactics, ensuring that platforms remain effective in contested environments. Cloud And Edge Computing Cloud infrastructures enable global data access and storage, while edge computing allows local processing on the battlefield. This hybrid approach balances speed with resilience, ensuring that operations continue even if connectivity is disrupted. Interoperability And Open Architectures Defense coalitions require software that interoperates across nations and branches. Open standards and modular architectures reduce vendor lock-in and make platforms adaptable to evolving mission needs. Challenges In Defense Software Platforms Despite advances, defense platforms face unique challenges that require disciplined engineering and strong governance. Cybersecurity Threat Landscape Defense networks are constant targets for state-sponsored attackers. Maintaining cyber resilience demands proactive patching, threat hunting, and integration of AI-based anomaly detection. Integration Of Legacy Systems Many defense organizations operate legacy platforms alongside modern systems. Achieving interoperability without degrading performance or security is a significant engineering challenge. Cost And Lifecycle Management Defense software platforms require sustained investment over decades. Lifecycle planning—covering development, deployment, upgrades, and decommissioning—ensures cost-effectiveness while preserving mission readiness. Industry Use Cases And Applications Defense software platforms are applied in diverse operational contexts, each requiring unique adaptations. Air And Missile Defense Platforms integrate radar, interceptors, and early-warning systems. Real-time tracking and AI-based threat classification support faster interception decisions and improved protection of critical assets. Naval Operations Maritime platforms coordinate fleet movements, anti-submarine warfare, and unmanned vessel integration. Advanced sonar and satellite connectivity extend operational reach into contested waters. Ground Operations Battlefield management software integrates soldier-wearable devices, armored vehicle sensors, and drone reconnaissance into a unified ground picture. This increases coordination and survivability in high-threat environments. Space And Satellite Operations Software platforms manage satellite constellations for communications, navigation, and Earth observation. Automated collision avoidance and resilient data links protect national assets in orbit. Why Bilgeweb Is A Trusted Partner Bilgeweb provides end-to-end defense software platform development with a focus on security, scalability, and interoperability. By combining deep expertise in industrial automation, AI integration, and mission-critical software, Bilgeweb ensures that defense clients receive solutions aligned with international standards and future-ready architectures. Secure By Design Every platform developed by Bilgeweb is built with cybersecurity in mind. From encryption protocols to intrusion monitoring, the company ensures that systems remain resilient under constant cyber pressure. Modular And Scalable Solutions Bilgeweb embraces open standards and modular frameworks. This guarantees that platforms can be extended with new capabilities—AI modules, data analytics engines, or interoperability layers—without disrupting existing infrastructure. Global Defense Experience With a track record in industrial, AI-driven, and Web3-integrated projects, Bilgeweb applies its cross-domain knowledge to the defense sector. The result is platforms that are not only functional but also adaptive to emerging technologies and threats. Defense software platforms are the foundation of modern mission success. With capabilities ranging from C2 to ISR, cybersecurity to simulation, they provide the digital backbone of national security. By partnering with Bilgeweb, defense organizations gain access to secure, future-ready, and innovative platforms that align with both present missions and long-term strategic goals.
Industrial Automation Engineering Services
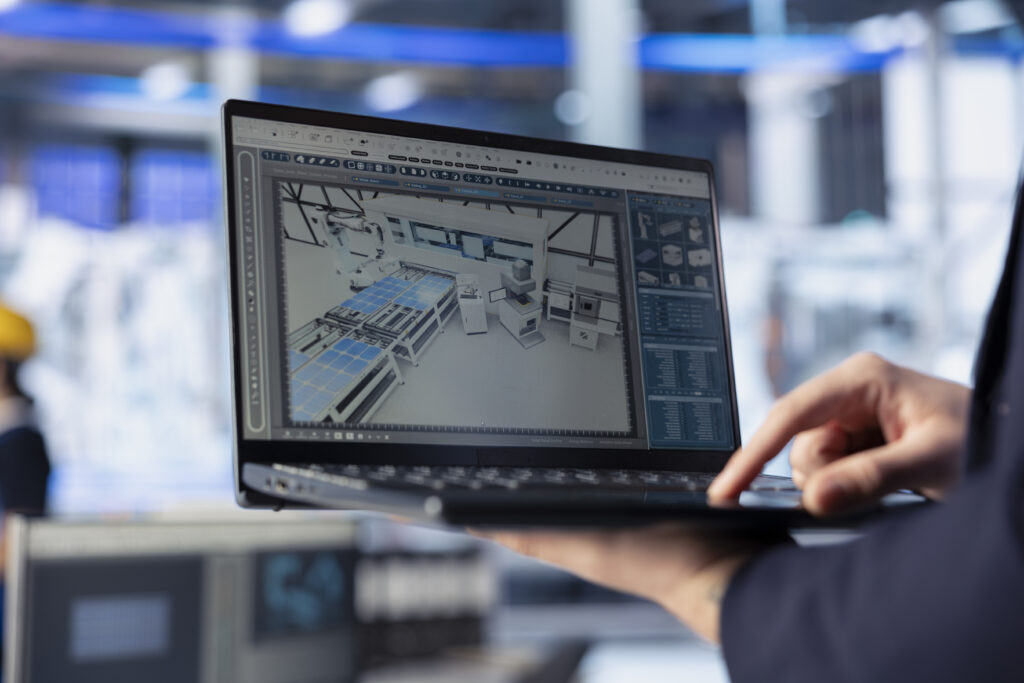

Scope Of Industrial Automation Engineering Services Comprehensive service spans the entire lifecycle of automated systems—from opportunity discovery to sustained optimization. A capable partner will cover controls, data infrastructure, machine safety, electrical design, and integration with enterprise platforms, ensuring that every layer plays together without finger-pointing or lock-in. Control Systems Engineering At the core is deterministic control of machines and processes. Engineers design PLC logic, state machines, and interlocks; build HMI screens that prioritize operator clarity; and implement alarm philosophies that minimize nuisance alerts. Typical platforms include Siemens, Rockwell, Beckhoff, and Delta. The goal is always the same: intuitive operation, predictable sequences, and safe failure behaviors that protect people and assets. Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition SCADA systems weave together distributed devices, lines, and utilities into a single source of truth. A well-architected SCADA provides real-time trending, alarm analysis, batch tracking, and contextualized events. With secure remote access and user role management, supervisors can intervene quickly, while andon boards and dashboards make production status visible on the floor. Robotics And Motion Robotic cells and coordinated motion reduce cycle time and ergonomic risk. Services include application study, reach and payload checks, end-of-arm tooling design, offline programming, and safety zoning with light curtains or laser scanners. For conveyors, gantries, and multi-axis stages, servo tuning and cam profiles ensure smooth acceleration, accurate positioning, and long component life. Industrial Vision And Quality Machine vision detects defects earlier and more consistently than manual inspection. From barcode and OCR validation to surface defect detection and dimensional checks, vision stations close the loop by feeding results back to the PLC or MES. Where suitable, classical image processing is combined with lightweight AI models at the edge to balance accuracy with latency and cost. Instrumentation And Data Acquisition Sensors translate physical reality into trustworthy signals. Engineers specify transducers for temperature, flow, level, torque, vibration, and pressure; assure proper shielding and grounding; and calibrate against traceable standards. Data is historized with rich context, enabling root cause analysis instead of guesswork. Electrical Design And Panel Fabrication Panels are designed for maintainability, heat management, and clear wiring routes. Compliance with IEC 60204-1 and relevant national codes is non-negotiable. Documentation—schematics, cable schedules, I/O lists, and bills of materials—is kept synchronized with the as-built state to prevent costly field surprises. Functional Safety And Risk Reduction Functional safety engineering ensures that the system remains safe even when components fail. Services include hazard analysis, performance level calculations per ISO 13849 or SIL determination per IEC 62061, safety device selection, and validation testing. A documented safety concept helps auditors and protects operators. Outcomes That Operations Leaders Value Automation projects must earn their keep. The most successful programs treat KPIs as first-class requirements rather than afterthoughts. Higher OEE And Stable Throughput By eliminating micro-stops, automating changeovers, and tightening feedback loops, Overall Equipment Effectiveness climbs. Lines run closer to nameplate capacity, with fewer surprises and faster recovery after faults. Better Quality And Less Rework In-process checks, recipe enforcement, and vision-assisted inspection reduce variability. When defects happen, automated genealogy and parameter history point directly to the cause, saving hours of trial and error. Energy And Utility Optimization Coordinated control of compressors, pumps, ovens, and HVAC based on real demand cuts peak loads and wasted idling. Energy per unit becomes a controllable metric rather than a fixed burden. Traceability And Compliance From raw materials to finished goods, automated tracking supports product recalls, customer audits, and industry regulations. Electronic records, e-signatures, and controlled access align operations with good manufacturing practice and digital audit trails. Execution Approach That Reduces Risk Great outcomes come from great process. A disciplined methodology shortens time to value and prevents scope drift. Opportunity Discovery And Process Mapping Workshops document current state, constraints, takt times, and bottlenecks. The team identifies automation candidates with clear problem statements and measurable benefits. Value stream maps highlight interfaces and buffer strategies across lines and utilities. Feasibility And ROI Modeling Financial models use baseline OEE, scrap rates, labor distribution, and energy intensity. Scenarios quantify payback under conservative and aggressive assumptions. This turns budget discussions into data-driven decisions. Architecture And Technology Selection Platform choices consider lifecycle cost, spares availability, staff skills, and vendor independence. Networking plans blend PROFINET, EtherNet/IP, Modbus, and OPC UA. For enterprise data, MQTT bridges and edge gateways decouple shop-floor protocols from cloud or on-prem analytics. Simulation And Digital Twin Discrete event simulation and physics-based models de-risk line layouts, buffer sizing, and robot reach. Virtual commissioning validates PLC logic and HMI screens before hardware arrives, shrinking onsite debug windows. Prototyping, FAT, And SAT Pilot cells validate assumptions with production parts. Factory Acceptance Tests verify interlocks, sequences, and alarms against a signed protocol. Site Acceptance Tests prove utility readiness, field wiring, safety circuits, and operator workflows under real conditions. Change Management And Training Operator adoption determines project success. Clear work instructions, layered process audits, and role-specific training build confidence. Maintenance teams receive schematics, spare parts lists, and guided troubleshooting trees. Lifecycle Support And Continuous Improvement After go-live, proactive services include patch management, vulnerability reviews, backup policies, and periodic performance audits. Small adjustments—such as alarm rationalization or PID retuning—often deliver outsized gains. Technology Stack And Best Practices Standardization reduces complexity, while open interfaces safeguard future choices. Programmable Controllers And HMIs Modern PLCs and soft PLCs handle deterministic logic and motion, while HMIs communicate intent through clean layouts, consistent colors, and state cues. Libraries of tested function blocks accelerate development and improve reliability. Industrial Networking And Data Robust networks use managed switches, VLANs, and QoS for time-critical traffic. Data moves through OPC UA and message brokers, with historians capturing events at sub-second resolution. Time synchronization across devices ensures that post-mortems are accurate. Cybersecurity For OT Defense-in-depth protects production from both accidents and adversaries. Segmented zones, least-privilege accounts, application whitelisting, and secure remote access reduce attack surface. Policies and monitoring align with IEC 62443 guidance. Machine Safety And Standards Alignment Risk assessments drive safety circuits, guard locking, and safe motion. Validation verifies that stop categories, muting, and reset logic match the design intent. Compliance is